Terminology for RNA Basepairs
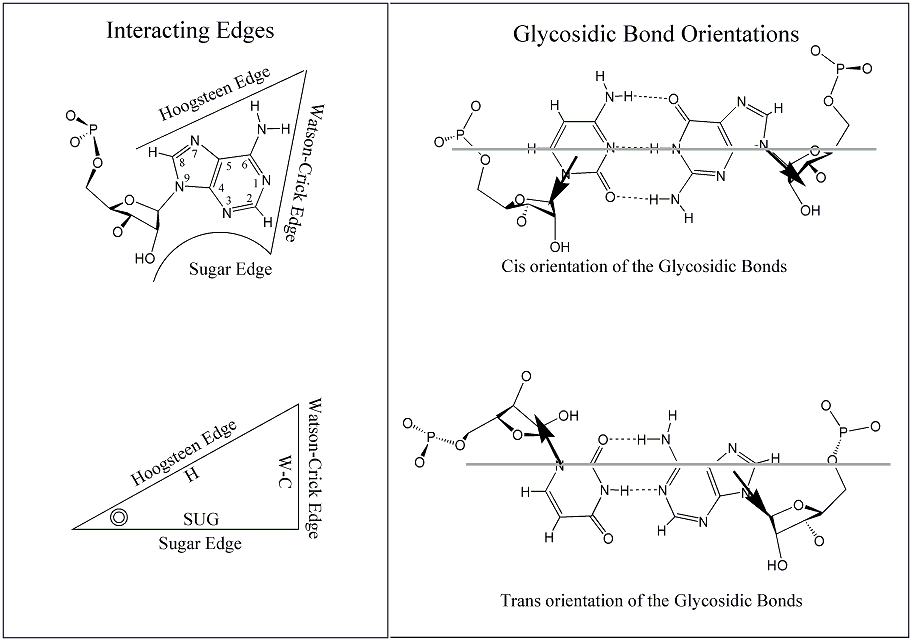
Figure: Base edges and Base-pair geometric isomerism. (Upper left) An adenosine showing the three base edges (Watson-Crick, Hoogsteen and Sugar-edge) available for hydrogen-bonding interactions. (Lower left) Representation of RNA base as a triangle. The position of the ribose is indicated with a circle in the corner defined by the Hoogsteen and Sugar edge. (Right) Cis and Trans base-pairing geometries, illustrated for two bases interacting with Watson-Crick edges. (Leontis & Westhof, 2001).
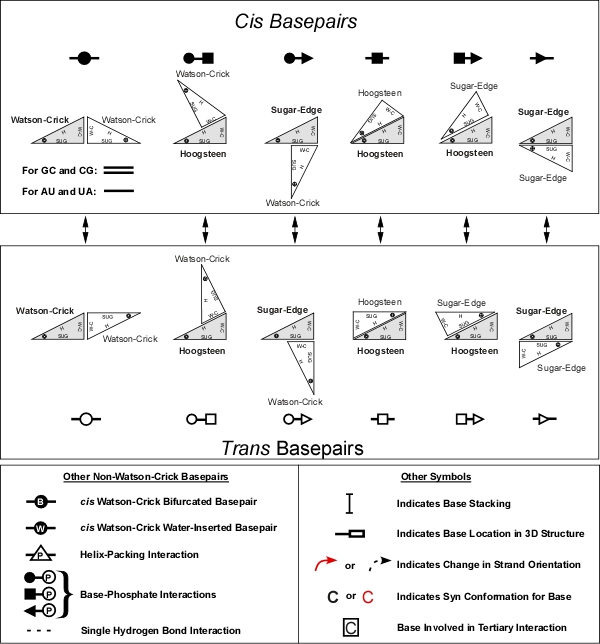
Figure: Basepairs geometric families and their annotation. Upper panel: Twelve geometric basepair families resulting from all combinations of edge-to-edge interactions of two bases with cis or trans orientation of the glycosidic bonds. Circles represent Watson-Crick edges, squares Hoogsteen edges, and triangles Sugar edges. Basepair symbols are composed by combining edge symbols, with solid symbols indicating cis basepairs and open symbol, trans basepairs. Lower Left: Symbols for other pairwise interactions. Lower Right: Additional symbols for base-stacking, reversal of chain direction in hairpin loops, syn bases, and bases forming tertiary interactions (Leontis et al., 2002).
1. Leontis NB, Westhof E. 2001. Geometric nomenclature and classification of RNA base pairs. RNA 7:499-512. Abstract
2. Leontis NB, Stombaugh J, Westhof E. 2002. The non-Watson-Crick base pairs and their associated isostericity matrices. Nucleic Acids Res 30:3497-3531. Abstract